Syndactyly or Fused Fingers
Syndactyly is a congenital condition where two or more fingers are joined together by skin or the bone or both. The degree of fusion can vary, and it may affect only the skin or extend to involve the bones and joints of the fingers. The fusion can occur in any part of the fingers and can be partial or complete. The condition can occur in both the hands and feet.
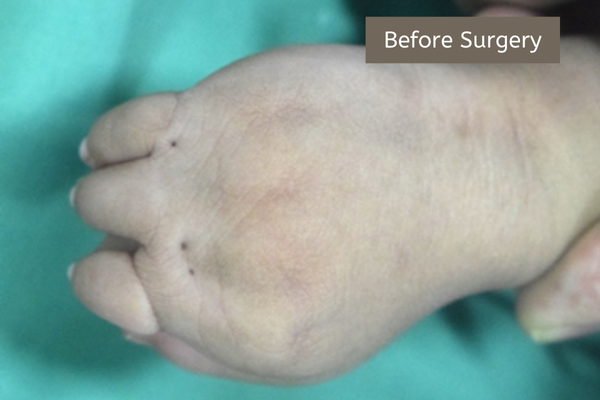
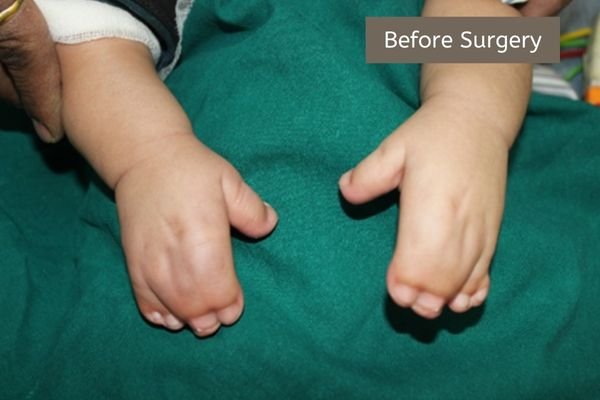
Two or more fingers may be fused with one another for varying lengths.
The child is born with two or more fingers fused into one mass. This is called syndactyly. The aim is to separate these fingers into their independent and individual entities. At times all the fingers are fused into one single mass. The aim is separation of the fingers. It should be borne in mind that two adjacent digits are not equal in length. Hence the probability of the fingers deforming further is higher. Surgery is undertaken to separate them and prevent further deformity. It should be done very early in life.
Types of Syndactyly:
- Simple Syndactyly: Only the skin is fused between the fingers.
- Complex Syndactyly: This involves the fusion of the bones and soft tissues. It may require more complex surgical intervention, involving the separation of the bones and the reconstruction of the web space.
- Complete Syndactyly: The fingers are fully fused together all along its length.
- Partial Syndactyly: The fingers are partially fused, with some separation still present between the digits.
Surgical Treatment:
The treatment for syndactyly is surgery, which is typically performed when the child is between 6 months to 2 years of age. Surgery aims to separate the fused fingers, creating functional web space between them to allow for better movement and hand function.
Key elements of surgery include:
Webspace creation: The skin is carefully divided to ensure the fingers are properly separated.
Skin grafts: If there is not enough skin to cover the newly separated fingers, skin grafts may be used.
Bone separation: The bones are surgically separated and realigned in more complex cases.
Nail fold reconstruction: This may be necessary to ensure the proper formation of the nail area after separation.
Post-Surgical Care and Outcome:
Follow-up: Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor healing and minimize joint stiffness. Customized dynamic splints are provided to overcome stiffness
We encourage all to ask questions about recovery. Would you like to discuss any specific cases or techniques related to syndactyly treatment?
What if the syndactyly is not surgically treated and separated early?
As you can see in below images, the two adjacent fingers grow at different rates. As the affected fingers grow, the discrepancy in the growth of the fingers causes further accentuation of the deformity of the fused fingers. This makes it extremely necessary to surgically treat the affected fingers early.
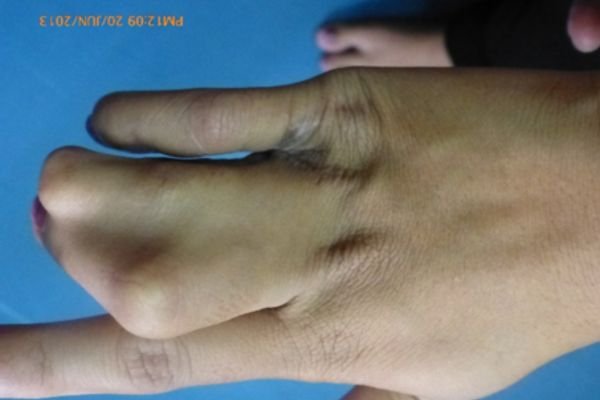
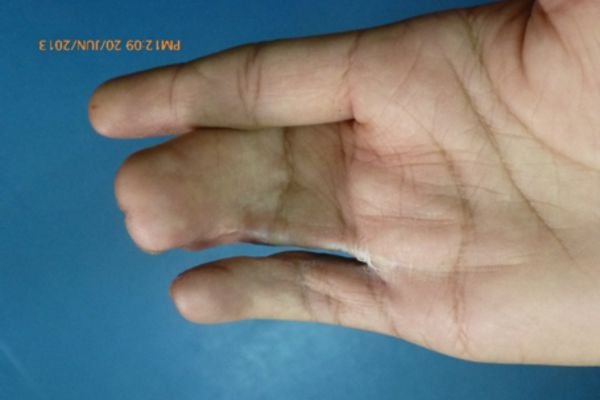
Syndactyly can present in various forms. A few examples are:
Syndactyly: Syndactyly is a congenital condition in which two or more fingers or toes are fused together. This fusion can involve just the skin (simple syndactyly) or also the bones, tendons, and other tissues (complex syndactyly). Syndactyly can affect one hand, one foot, or both, and the degree of fusion can range from partial to complete.
The condition can occur as an isolated feature or as part of a broader syndrome, such as Apert syndrome or Crouzon syndrome. In mild cases, the fused digits may not cause significant functional problems, while in more severe cases, the fusion can affect movement and grip, causing challenges in daily tasks.
Treatment typically involves surgical separation of the fused digits, often performed in early childhood to improve both appearance and function. The goal of surgery is to restore normal finger or toe function while minimizing scarring. Post-surgical rehabilitation, including physical therapy, may be recommended to improve mobility and strength in the affected digits. Early intervention is important to achieve the best possible functional and cosmetic outcomes.
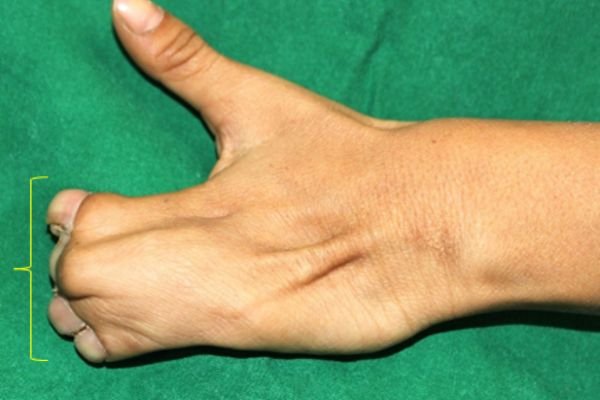
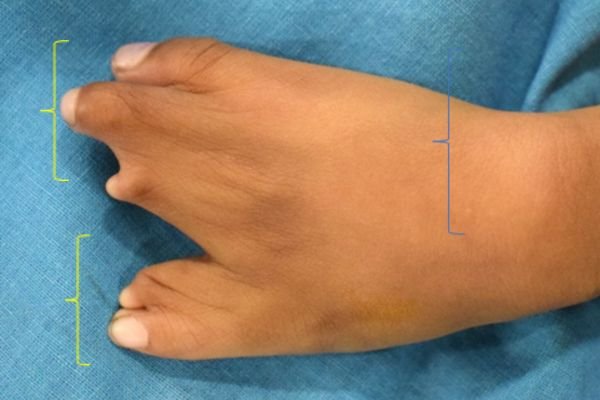
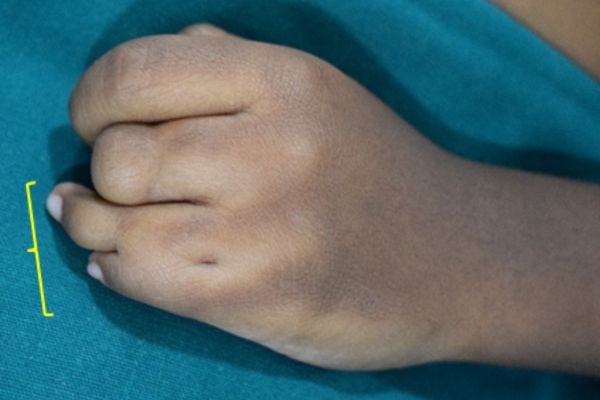
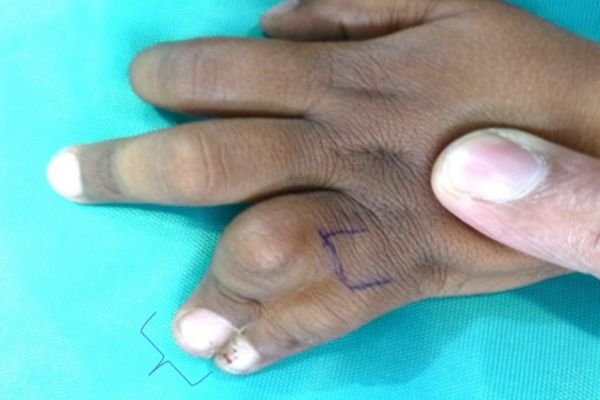
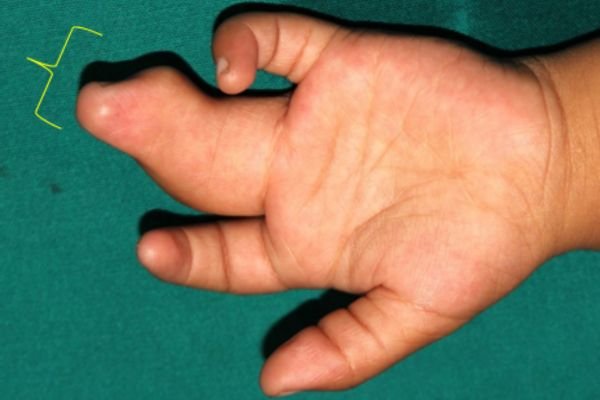

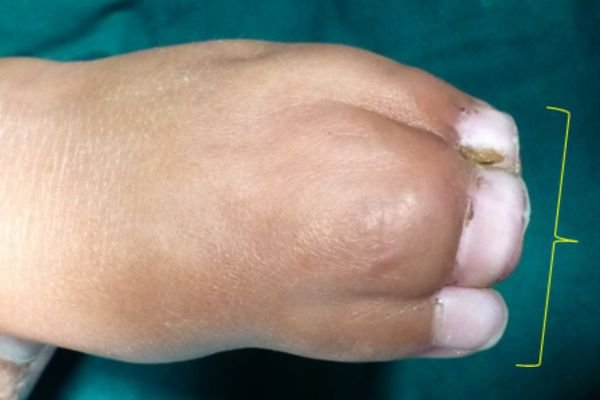
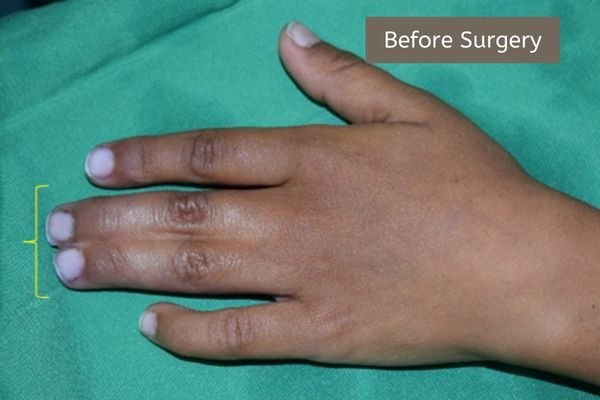
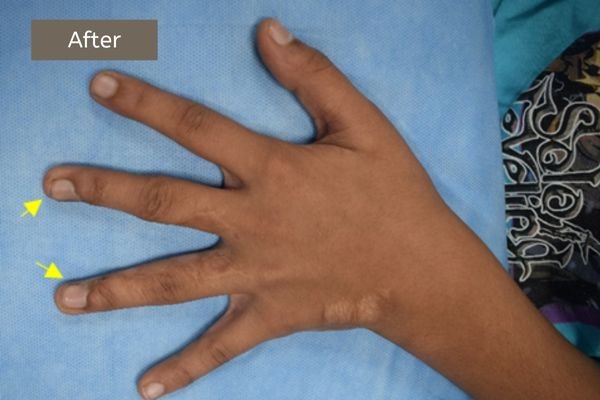
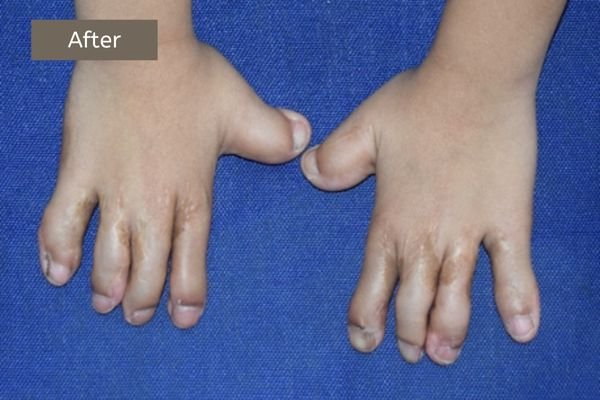
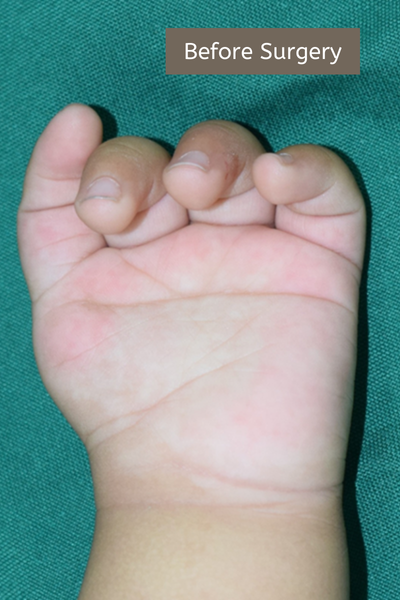
Example 1. An example of surgery and the result.
The child had surgery to separate the fused index finger from the middle finger. With the excellent results that followed, he opted for another surgery to separate the ring finger from the middle finger.
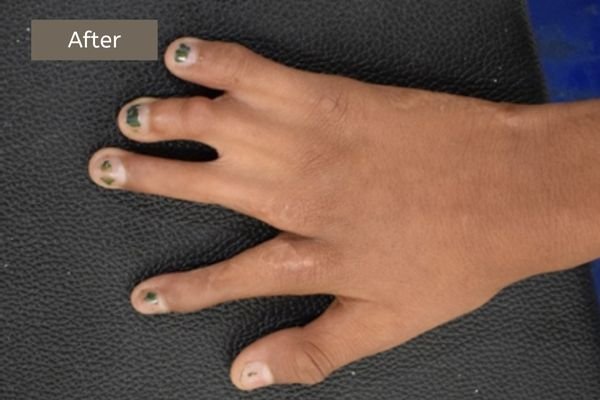
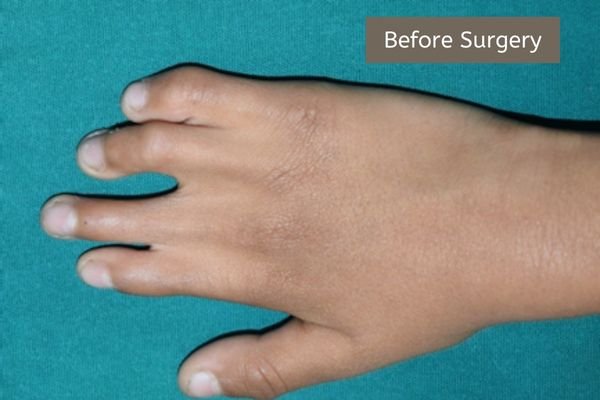

Example 2: Another example of fused fingers and the result of surgery. The middle and the ring fingers have been fused since birth. They were surgically separated.
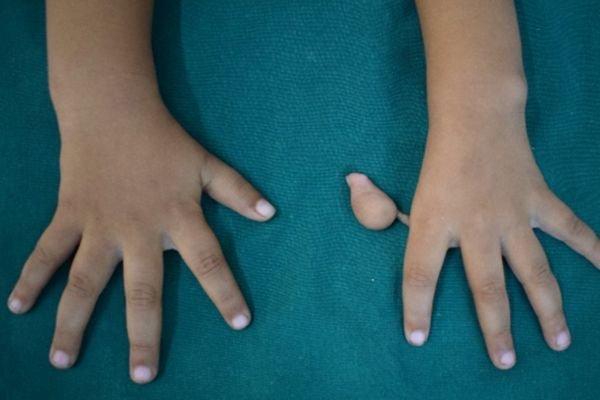
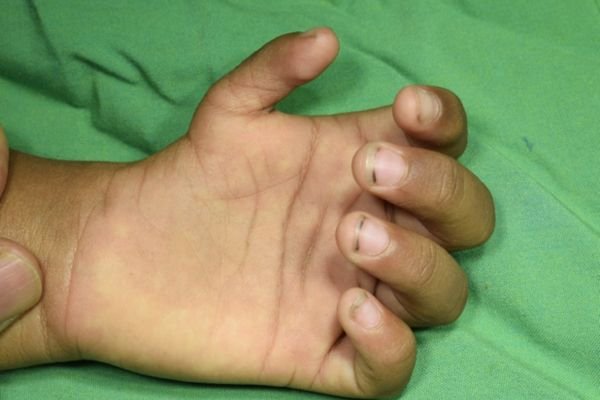
Example 3: An example of a complex case of fused fingers. The fingers were surgically separated to create a 5-fingered normal hand.
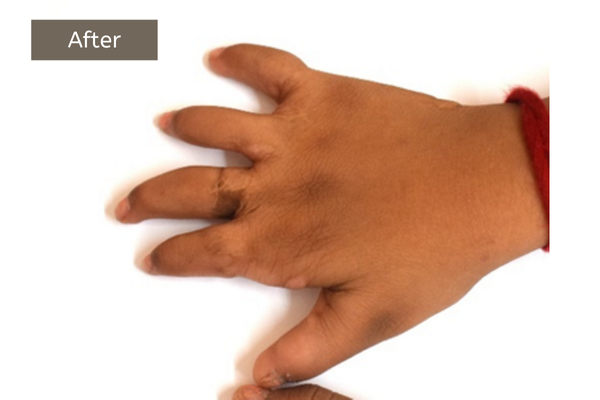

Apert Syndrome
Apert Syndrome: Apert syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the development of the skull, face, and hands. It results in a misshapen head and facial abnormalities. This condition can also associated with syndactyly, where the fingers and toes are fused, leading to webbed or joined digits.
In individuals with Apert syndrome, cranial abnormalities can cause at times developmental delays, intellectual affection, and hearing loss. Additionally, facial features may be affected, with a broad, flat face, shallow eye sockets, and a beaked nose.
The condition also often includes hand and foot deformities, where the fingers and toes may be fused or abnormally shaped. This can impair hand function, and often needs, reconstructive surgeries to separate the digits and improve functionality.
Absent Thumb
Absent Thumb: An absent thumb, also known as thumb aplasia, is a congenital condition where the thumb is missing from one or both hands. This condition can occur alone or as part of a broader hand or limb anomaly, such as radial club hand. The absence of a thumb significantly affects hand function, as the thumb plays a critical role in gripping, pinching, and performing fine motor tasks.
Treatment for an absent thumb focuses on restoring hand function by creating a thumb. One common surgical approach is pollicization, where the index finger is reshaped and repositioned to function as a thumb. In a delicate surgery, the thumb is reconstructed by shifting the index finger at the location of the thumb. Essentially this means instead of 4 fingers and no thumb, the child has three fingers and a functioning thumb which provides a very rewarding, useful, and enhanced hand function This procedure is usually performed in early childhood, when the hand is still developing, to allow the child to adapt and gain optimal function.
Early evaluation by a specialist is essential to plan the most effective treatment, which also includes adaptive techniques to enhance the hand’s functionality
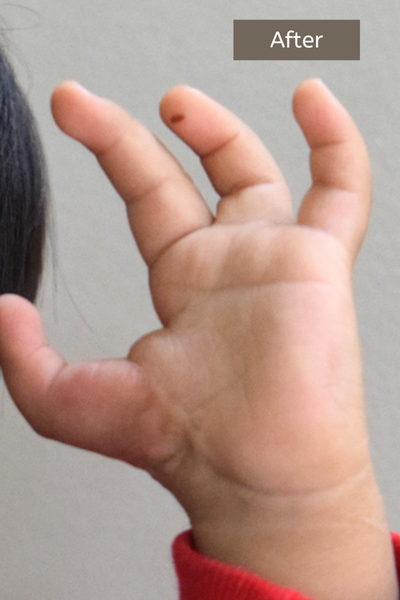

Hypoplastic Thumb (Inadequately Developed Thumb)
Hypoplastic Thumb: A hypoplastic thumb is a congenital condition where the thumb is underdeveloped and smaller than normal. This can range from mild cases, where the thumb is slightly smaller but functional, to severe cases, where the thumb is weak, unstable, or barely formed. In some instances, the thumb may lack essential structures like muscles, tendons, or bones, making it difficult to use effectively.
Hypoplastic thumbs often affect one or both hands and may be associated with other congenital conditions, such as radial longitudinal deficiency. The condition can impact hand function, particularly in tasks requiring grip or pinch strength.
Treatment depends on the severity. Mild cases may be managed with therapy or splinting to improve strength and stability. Severe cases often require surgery, such as reconstructive procedures to stabilize or enhance the thumb. In extreme cases, pollicization (reconstructing the thumb using the index finger) may be performed to restore hand functionality. Early intervention ensures better outcomes for both function and appearance.
Example 1.
Hypoplastic Thumb (Poorly developed thumb). The thumb is poorly developed and attached with a very tiny lifeline, the thread of skin as shown by the arrow.
Example 2:
The thumb is poorly developed. It is small, contracted, and can deviate in other directions due to poorly developed attachments called ligaments.
The span between the thumb and the index is also narrow.
Example 3:
The arrow points at the poorly developed thumb. The other normal hand is a ready reference for easy comparison of the size.
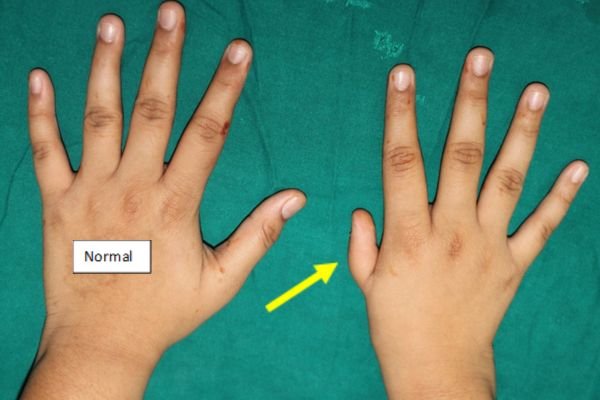
Macrodactyly (Giant Finger) / (Gigantism) (Large Finger / Thumb)
Macrodactyly: Macrodactyly is a condition characterized by the abnormal enlargement of one or more fingers or toes, This enlargement is due to overgrowth of the tissues, such as bones, skin, nerves, and blood vessels, and may affect a single digit or multiple digits. The enlarged finger or toe may appear disproportionately larger than the others, and in severe cases, the affected digit can be much thicker or longer.
Macrodactyly can be present at birth (congenital) or develop later in life (acquired). The condition can be caused by genetic factors, or it may occur as part of other syndromes, such as Neurofibromatosis or Maffucci syndrome.
The condition can lead to functional issues, including difficulty with fine motor skills, pain, and cosmetic concerns.
Treatment depends on the severity and impact of the condition and includes surgical intervention to reduce the size of the affected digit, improve function, or address associated deformities. The giant index finger is shaped and shortened to look with a normal proportion. The nail is preserved.
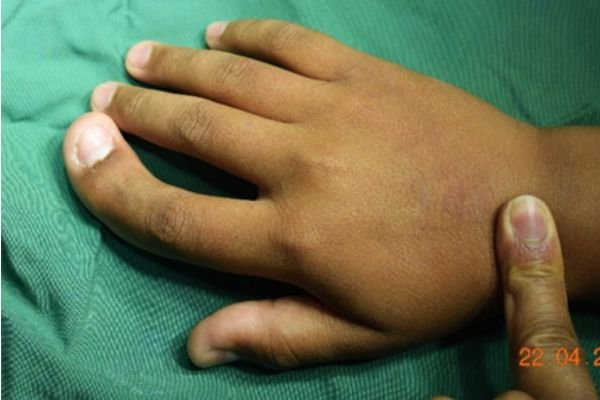
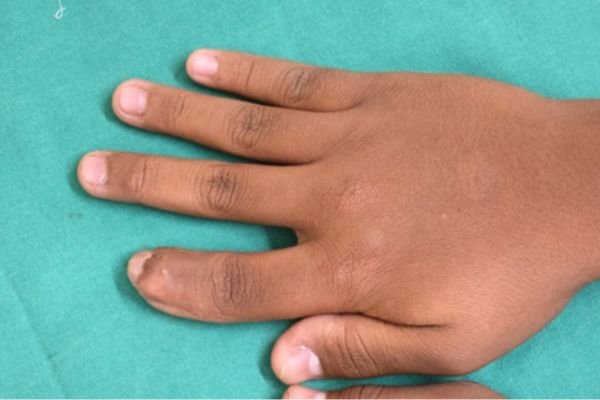
Polydactyly (Duplication Of Fingers)
Duplicate Thumb: Duplicate thumb, also known as thumb duplication or polydactyly of the thumb, is a congenital condition where a person is born with two thumbs on the same hand. The duplicated thumb can range from a small extra nub to a fully formed additional thumb, and both thumbs may vary in size, alignment, and functionality.
This condition is often noticed at birth and can occur in one or both hands. While it may not cause pain, the presence of an extra thumb can affect the cosmetic appearance of the hand and interfere with activities requiring a strong or coordinated grip.
Treatment usually involves surgery, ideally performed during early childhood, to remove the extra thumb and reconstruct the remaining one. The goal is to create a single, well-functioning thumb that looks natural and works effectively for daily tasks. Early intervention helps ensure better outcomes for both hand function and appearance.
We encourage discussion with the affected person and his family regarding the had and its appearance.
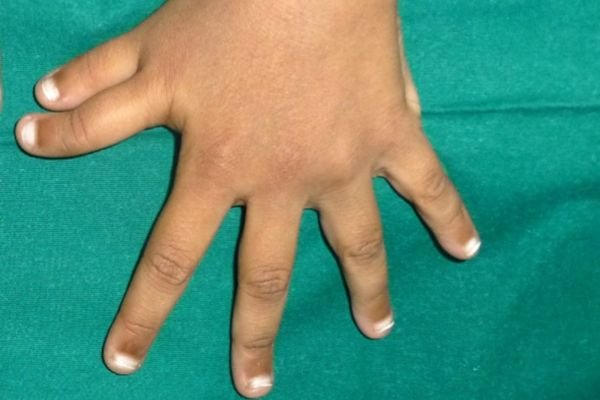
Camptodactyly (Bent Finger)
Camptodactyly: Camptodactyly is a condition where one or more fingers, typically the little finger, are permanently bent and cannot fully straighten. This bending occurs at the middle joint of the finger (the proximal interphalangeal joint) and is often noticed during childhood or adolescence. It can affect one or both hands and may vary in severity from mild to more pronounced deformity.
The condition can result from tight skin, abnormal tendons, or imbalanced muscles around the affected joint. While Camptodactyly does not usually cause pain, it may interfere with hand function, especially in severe cases.
Treatment depends on the severity and impact on daily activities. Mild cases may not require intervention, while moderate cases can benefit from dynamic splinting and physical therapy to improve flexibility and prevent worsening. Severe cases or progressive deformities may require more extensive surgical intervention to release tight tissues, adjust tendons, or improve joint function. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further stiffness and improve hand function.
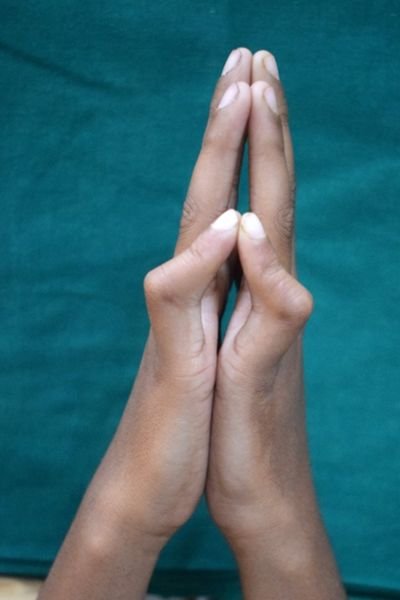

Radial Club Hand (Bent Forearm)
Radial Club Hand: Radial club hand, also known as radial longitudinal deficiency, is a rare congenital condition where the radius (the bone on the thumb side of the forearm) is underdeveloped or missing. This leads to the hand and wrist curving toward the thumb side, giving the arm a shortened or angled appearance. The thumb may also be small, underdeveloped, or completely absent.
The condition can affect one or both arms and may range from mild to severe. Radial club hand can make it challenging to use the hand for everyday tasks like gripping or holding objects, depending on the severity of the deformity.
Treatment aims to improve both appearance and function. In infancy, stretching exercises and splinting are often used to correct wrist positioning. Stretching is done within the tolerance of the infant byte mother under the instructions of the surgeon and the therapist. For more severe cases, surgical options such as external Fixation to stretch the tissue further followed by centralization or radialization of the wrist, tendon transfers, or thumb reconstruction which can help restore alignment and functionality. Early evaluation and intervention are crucial to ensure the best possible outcomes and support a child’s development
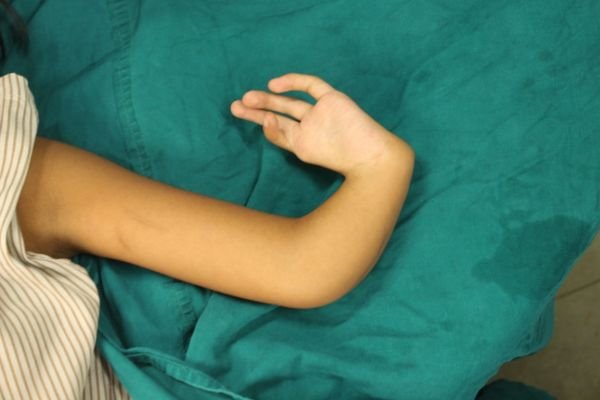
Triphalangeal Thumb (Longer Thumb)
Triphalangeal Thumb: A triphalangeal thumb is a rare condition, where the thumb has three bones (phalanges) instead of the normal two, giving it a longer and sometimes finger-like appearance. This condition is usually present from birth and can occur in one or both thumbs. It may be inherited, with a family history of similar thumb shapes.
A triphalangeal thumb can cause difficulty in performing fine motor tasks like pinching or gripping, as the thumb may lack its typical flexibility and strength. In some cases, the extra bone can also cause deformities, such as the thumb curving abnormally.
Treatment depends on how much the condition affects hand function. Mild cases may not require any intervention, while more severe cases might benefit from splinting, physical therapy, or surgery to remove the extra bone and restore the thumb’s function and shape. Early diagnosis and treatment can help ensure better outcomes and improve the thumb’s usefulness in daily activities.
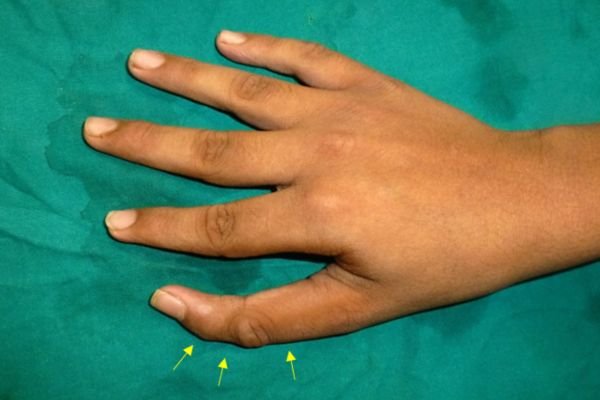
Aplasia Fingers (Absent Fingers / Non-Development of Fingers)
Aplasia of Fingers: Aplasia of fingers is a congenital condition where one or more fingers fail to develop fully, leading to missing or underdeveloped digits. This condition can affect part of a finger or the entire finger and may occur in one or both hands. It is often noticed at birth and may be isolated or part of a broader hand or limb anomaly.
The condition can limit hand function, particularly in tasks requiring gripping, pinching, or fine motor skills.
Treatment focuses on maximizing function and improving appearance. In young children, phalangeal transfer—a surgical technique where small amount bones from the toes are used to reconstruct the missing finger bones.
Early intervention usually around the first birthday with phalangeal transfer helps restore functionality during critical stages of growth and development.
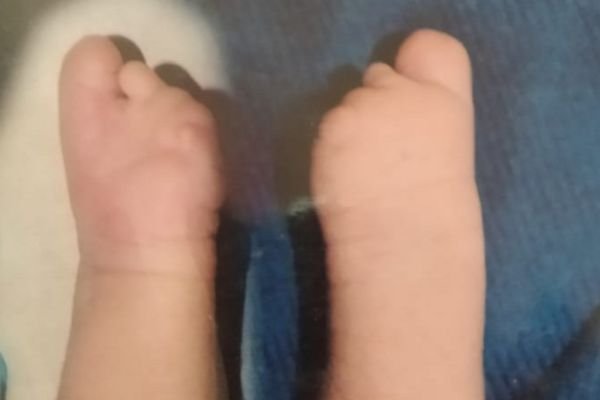
Central Deficiency (Deep Cleft in the Hand)
Central Deficiency Hand: Central deficiency hand, also known as central longitudinal deficiency or cleft hand, is a rare congenital condition where the central part of the hand (usually involving the middle fingers) does not develop fully.
This can result in a V-shaped cleft in the palm, with missing or underdeveloped fingers, while the thumb and little finger are typically more normal.
The condition can affect one or both hands and varies in severity, from minor finger abnormalities to more pronounced clefts. It may impact hand function, such as gripping or holding objects, depending on the extent of the deficiency.
Treatment focuses on improving hand function and appearance. Options include physical therapy to strengthen the hand and, in some cases, reconstructive surgery to close the cleft, improve finger alignment, or enhance overall hand function. Early intervention can help children adapt better and perform everyday tasks more easily
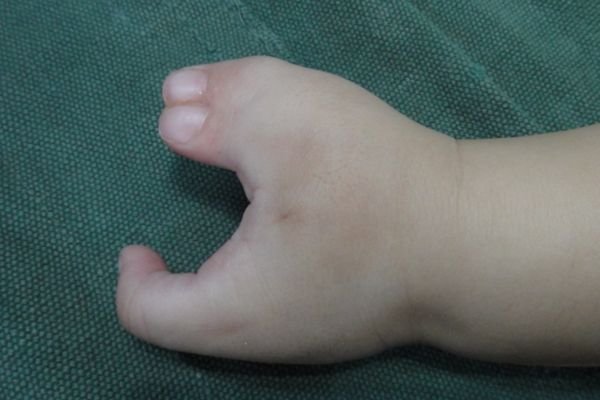
Spoon Hand
This complex deformity requires staged surgery to separate these fingers
The surgery involves:
- Creating a web so that the two fingers are separated by a U and not a V
- Creating a nice nail fold.
- To prevent fingers contracting due to skin deficiency
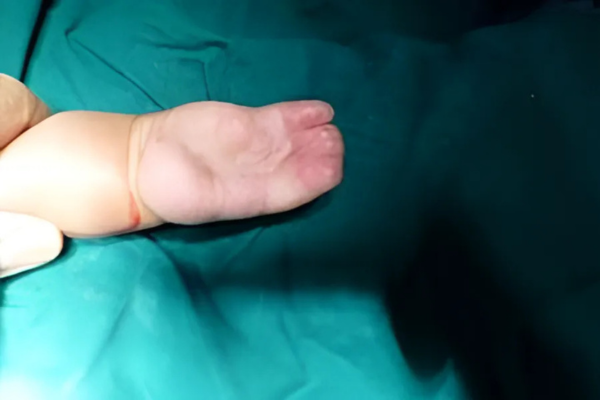
Central Defect
The central finger is missing and the first web is narrower.
Treatment:
The surgery entails: Shifting the index finger in such way to increase the first web space, and reduce the central wide space.
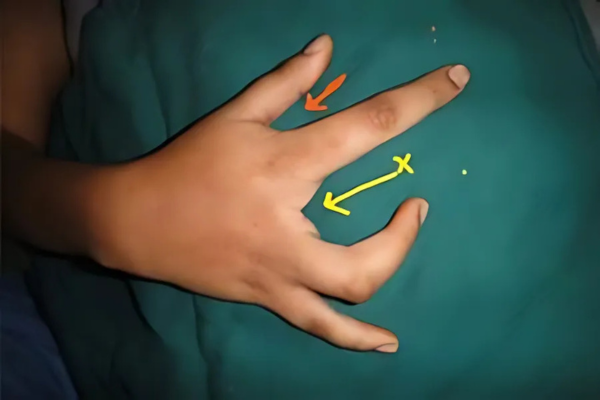
Floating Thumb
This is a severe type of thumb mal development. The thumb is poorly developed. It has no bone, no tendon and is hanging like a pendulum. Any effort at trying to save it is futile, as it has no representation in the brain and hence does not work. The best strategy is to transfer the index finger and create a new thumb (Pollicisation).
If the parents insist than we fix the floating thumb and make it sturdier but it stands out but does not serve any useful purpose and does not participate in the act of holding objects.

Polydactyly or Extra Fingers or Extra Thumb.
The mother and the daughter had similar deformity. The mother did not seek treatment but brought the daughter for surgery.
The aim of the surgery is to remove the extra digit, recreate the balance in the joint (Transfer the collateral ligament) by taking some tissue from the digit which is to be excised, and transfer of the tendon if needed.
Polydactyly & Duplicate thumb
The aim of the treatment is to create one single normal-looking thumb. This kind of duplication may be at the level of the terminal bone-like shown here or more proximally. At times it may involve the joint as well.

Transforming Lives with Congenital Deformity Care
Book Your Appointment Now!
CALL: +91 98220 31140
Frequently Asked Questions
While it may seem minor, untreated Blue Finger can lead to complications like permanent damage or loss of functionality.
Yes, by avoiding prolonged exposure to cold, managing stress, and seeking timely medical care for hand injuries
Recovery varies depending on the severity and treatment method but typically ranges from a few weeks to a few months.
