Fracture
Fractures








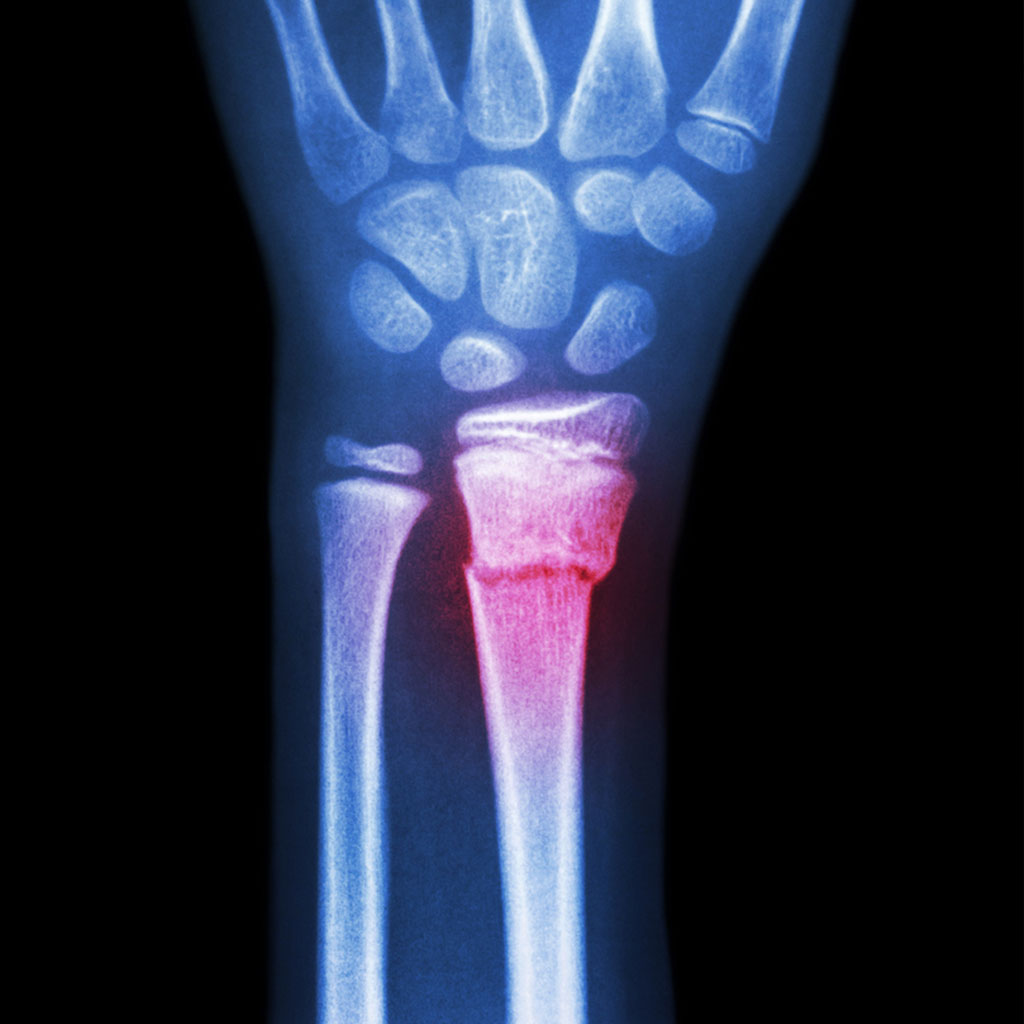




Fracture distal radius
Earlier known as Colles’ fracture, this is a fracture of the distal inch of the radius bone. It is one of the commonest fractures. Majority of times, it follows a trivial fall or on other occasions, it may follow a high-velocity injury like a motorcycle accident or a fall from a height. In the later situation, it is necessary to look for more injuries in other parts of the body.
Symptoms
The fracture mostly results in deformity of the wrist with Significant pain and swelling. The movements of the wrist may be painful. In spite of absence of Significant pain and deformity there may still be an undisplaced fracture.
Investigation
X-Rays of the wrist and the forearm are obtained. The X-Rays reveal the extent of the deformity. At times, CT scan or MRI Scan are required. When the fracture has resulted in multiple pieces, it is called as comminuted fracture.

Treatment

Plaster cast
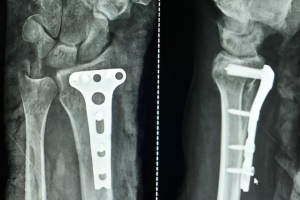
Plating

Kirschner wires
- The displacement of the fracture fragments may be insignificant. In such a situation, the surgeon may suggest a plaster immobilisation.
- If the fracture is displaced, they are manipulated back into alignment. To make this manipulation painless, some kind of local anaesthesia also called as regional anaesthesia is needed. The patient is taken to the well-equipped operation room. The operation room has a machine which is called as an image intensifier or a C’ arm. This machine gives x ray pictures of the bones in real time and instantly.
- When the pieces are displaced but are not comminuted, a good option may be fixation of the fracture with stainless steel sticks called Kirschner wires or K’ wires.
- At times, the fracture of radius may cause the wrist bones or carpus to slide out of alignment. These are called Volar Barton fractures and need open surgery and fixation with plates.
- On other occasions, there may be injury to adjacent bones and ligaments, needing additional treatment.
- An important consideration in deciding the treatment option is the amount of crushing of the bone, technically called as comminution. Other parameters are the amount of displacement of the fracture fragments, other associated injuries, the age of the patient.
- The plates currently available are made of either stainless steel or Titanium. They are pre contoured to fit the contour of the fractured bone. Over the years, the quality of plates has improved significantly. The size of the screw is about 2.4 to 2.7 mm in diameter.
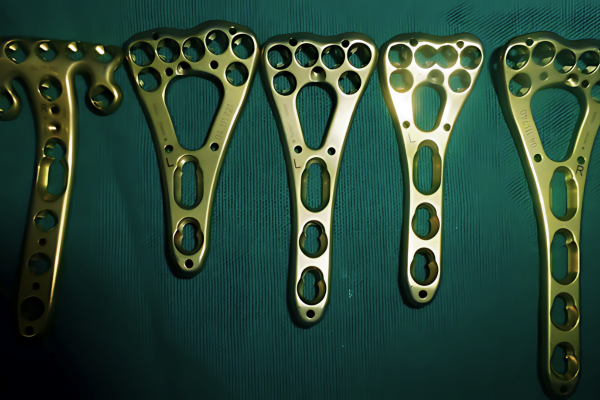
Titanium plates
Earlier known as Colles’ fracture, this is a fracture of the distal inch of the radius bone. It is one of the commonest fractures. Majority of times, it follows a trivial fall or on other occasions, it may follow a high-velocity injury like a motorcycle accident or a fall from a height. In the later situation, it is necessary to look for more injuries in other parts of the body.


Malunion: If the treatment is delayed, and the fragments are displaced, the fracture will unite in abnormal position. This is called malunion. Malunion may restrict the wrist movements and may be painful, affecting day to day working. If symptomatic, malunion needs surgery. The malunited bones are re fractured and deformity corrected and fixed.
Rehabilitation: The fracture fixation is one part of the treatment. The second part requires mobilisation of the joints. This is time consuming and require use of dynamic splints.
Fracture dislocation of proximal interphalangeal joint
In a cricket-playing country like India, fracture-dislocation is a common injury. The ball hits the tip of the finger. This leads to one or more fractures in the finger.

Diagnosis
An x-ray reveals, loss of alignment of the bones. Interpreting the x-ray properly helps to avoid missing the diagnosis. At times, the report accompanying the x-ray film may be erroneous, misleading and delays establishing the correct diagnosis. A good quality x-ray image with the appropriate position of the finger and magnification will show loss of collinear phalanges. Once the loss of alignment is established, the next step, is to assess the extent of joint affection and whether the fracture has resulted in gross multiple pieces (comminution).
Treatment
Several methods of treatment are available. The common methods of treatment include:
Close reduction
Extension Blocking Pins
Close reduction and internal fixation with one or more wires
External fixation in the form of Suzuki frame or its variants
Hemi hamate interposition arthroplasty
Volar plate interposition

Surgical step of Volar Plate Interposition
Earlier known as Colles’ fracture, this is a fracture of the distal inch of the radius bone. It is one of the commonest fractures. Majority of times, it follows a trivial fall or on other occasions, it may follow a high-velocity injury like a motorcycle accident or a fall from a height. In the later situation, it is necessary to look for more injuries in other parts of the body.


Hemi hamate replacement is an excellent method and is indicated when the injury involves extensive crushing(comminution). A piece of cartilage bearing bone is harvested from one of the wrist bones and fixed at the place of the damage using fine screws. Hemi hamate graft has also been used when the patient presents late and the joint has been locked in extension. Capitate is also used at times instead of Hamate. It has been done by us for over 10 years and all patients continue to do well.
Scaphoid fracture
Scaphoid is one of the eight bones in the wrist joint, located roughly where the base of the thumb connects to the forearm.
Symptoms
Following a fall on the outstretched hand, the person will develop a swelling, though insignificant, at the base of the thumb over the wrist. Pain may often not be much. The insignificant swelling and pain may be presumed to be a sprain and but is not so and should not be neglected.
Signs
There will be tenderness in the anatomical snuff box. There may be tenderness over the front of the wrist as well over the scaphoid tubercle.
Investigation
X-rays with special views are needed to confirm the diagnosis. These are called Postero- Anterior or PA view with ulnar deviation of the wrist and closed fist. This is also called as Scaphoid view. A few more views will be needed. At times CT scan and MRI are needed. Routine x rays called PA and lateral may often miss the fracture of the scaphoid bone. It is equally important to get magnified images of the scaphoid.

Treatment
The fractures which are undisplaced and located in the waist of the bone or near the tubercle of the scaphoid can be treated without surgery with application of a plaster cast.
If the fracture is displaced, shattered, delayed diagnosis, or involves other joints, it often requires surgical intervention. The fracture can be fixed with Kirschner wires, or Titanium screws or plate. Bone graft is added at times. The bone graft is mostly obtained from the wrist itself , at times it is harvested from the waist.
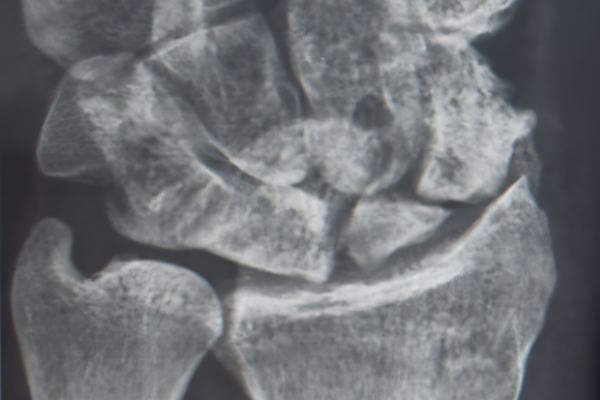


Proximal pole Fracture: Proximal pole fracture of the scaphoid is an entity which requires early intervention and surgery.
Avascular Necrosis: At times, the MRi may be asked for. The accompanying report may mention a word “Avascular Necrosis”. In simple words, it means, the fracture fragment has poor blood supply.
Non union: The scaphoid bone is notorious for not uniting if untreated or inadequately treated. This requires bone grafting and fixation with screw or wires. Once it was recommended to use vascularised bone graft. But scientific evidence suggest it is not required. Conventional Bone graft is good enough.
If fracture of the scaphoid does not unite, the fracture can progress in a set pattern over the next few years. This set pattern is called Scaphoid Non-Union Advanced Collapse or SNAC wrist. This needs surgical intervention.
Fracture Hamate
Fracture of the hamate is not a very common fracture. Following an injury, the hamate bone can rotate by 180 degrees! By open reduction, the fractures are brought back into alignment and fixed with wires. The wires were removed after a few weeks.


Fracture Hook of Hamate
is not a very common condition. The patient presents with pain in a small focal area on the palmar aspect of the hand, just distal to the wrist crease but in line with the ring finger. X-ray called carpal tunnel view may at times pick up the fracture. If this does not help, and a strong suspicion exist about the diagnosis, one may require a CT scan to diagnose the fracture of the hook.
The fracture may irritate the ulnar nerve (Ulnar nerve neuropathy) and cause tingling in the small finger or even weakness. The fracture often require surgery. Either fixation or excision of part of the bone (HAMATE) alleviates the symptoms.


This tennis player had fracture of hook of the hamate. It needed surgery to excise the offending bone. It heals without any residual deficit.
Capitate fracture
The capitate can get fractured and rotate by 180 degrees. Also called Fenton’s fracture. This needs surgical intervention.
Perilunate dislocation
The eight bones of the wrist have a set pattern of files and rows. Following a violent fall, the bones and ligaments break and this pattern becomes disorderly. Numerous signs are known. “Piece of Pie” sign to name just one.

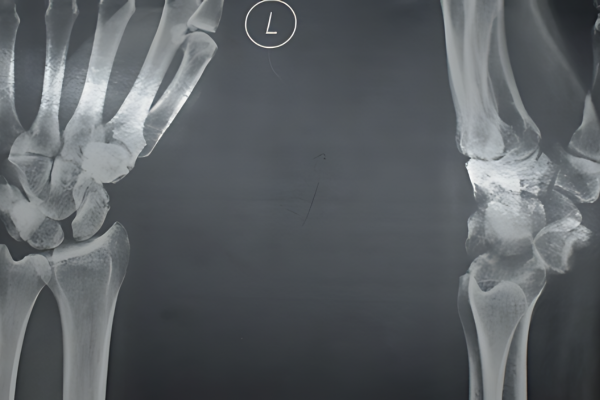

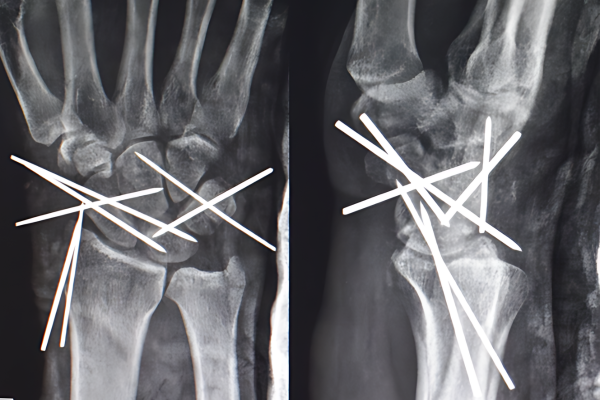
If there are assocaited fractures , they need to be fixed as well. The injury may damage the bones or the ligaments. Accordingly ,it is called Greater arc injury or Lesser Arc injury.
They may also be called Perilunate injury or Transscaphoid perilunate injury or similar other name. The word transe is used when more bones are involved.
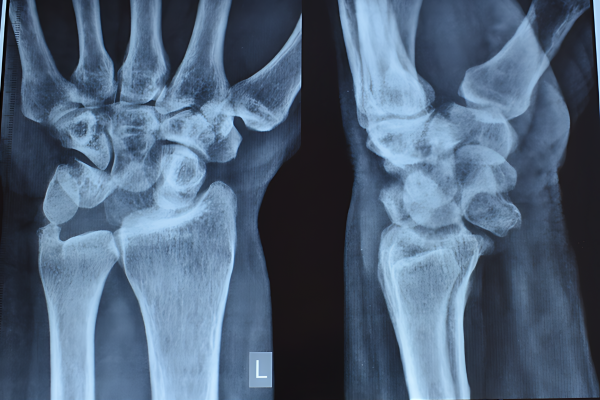
Surgical step of Volar Plate Interposition
At times, the injury to the wrist bones may remain undiagnosed for long time. With the passage of time, the bones ger further damaged and deteriorate , needing a different kind of salvage surgery where a row of bones has to be removed .This is called as Proximal row Carpectomy or PRC.

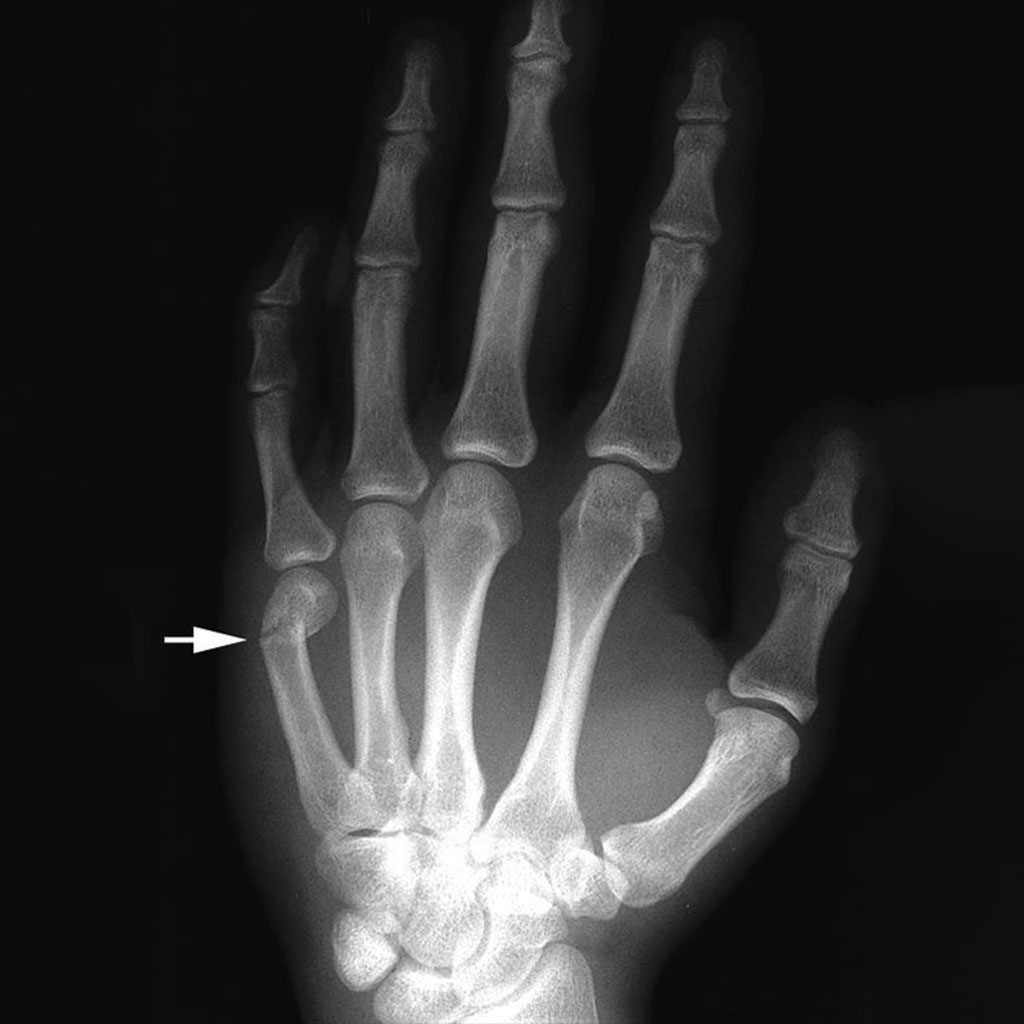
Bennett Fracture. Intra articular fracture of the base of the first metacarpal
A fracture of the base of the first metacarpal extending into the joint and splitting apart a part of the base is called a Bennett’s fracture. The two fragments are under constant traction in opposite directions. This makes the fracture highly unstable making surgery mandatory.

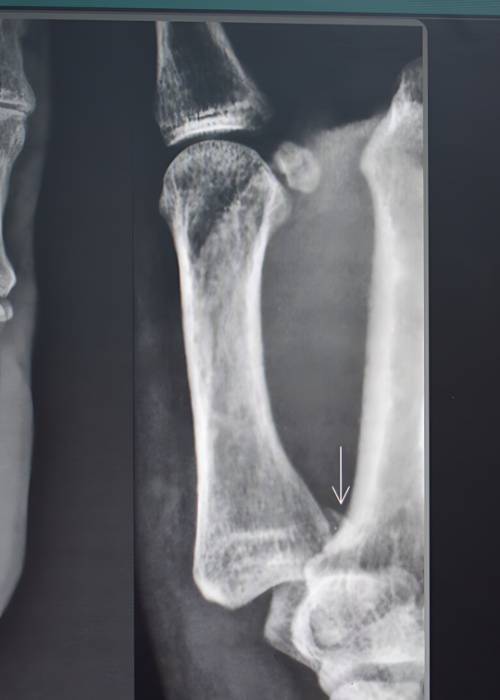
If the fracture results in multiple pieces, it is called as Rolando Fracture. This is treated with an external fixator or plate or wires.
If the fracture of the first metacarpal results in angulation it is called Epibasal fracture. This need correction to reestablish the span of the first web space.



Fracture Phalanx
Each finger has three phalanges. The thumb has two. They are all prone to get injured.
- Fracture of the phalanx may be displaced or undisplaced.
- There may be deformity, angulation, scissoring, shortening or an open fracture.
- If there is no deformity, the phalangeal fracture can be treated non operatively.
- Otherwise, they need surgery. Fixation can be done using wires, plates or External Fixation. Each method has its advantage.
- The fracture which does not involve the joint and does not have any deformity can be treated without surgery.
- If the fracture involves a joint ,surgery is very likely.
- Early movements and Rehabilitation are key to successful outcome.


At times, the joints can become very stiff, after surgery and need Dynamic Splinting or another surgery to restore hand movements. Rehabilitation is therefore very crucial.
Fracture Fifth Metacarpal or Boxer’s fracture:


Fractures of the fifth metacarpal occur following a fist striking a hard object. Significant angulation needs correction of the deformity by passing wires across the fracture. There are a few more reason for surgical intervention. If multiple bones of the same hand are injured, it is an indication for surgery. Open fracture or a compound injury is also an indication for surgery.
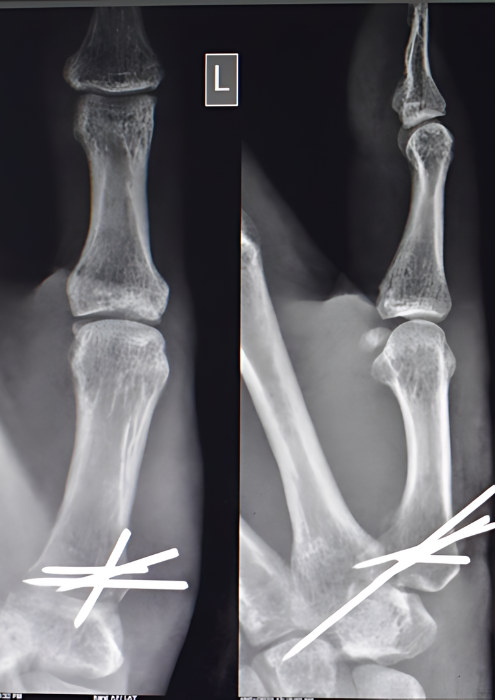
Finger Fracture
The child sustained fracture to his fingers. The fractures were brought back to their alignment.
Case Study

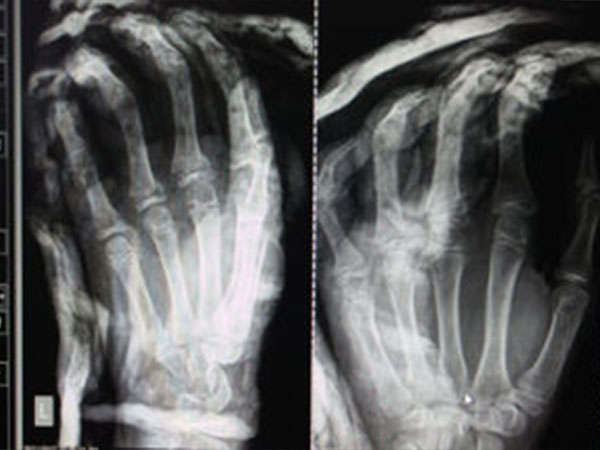

A fracture of the fifth metacarpal as depicted here is called a Boxer’s fracture. It occurs following hitting a hard object. The treatment varies from a plaster support to surgical restoration depending on the extent of the deformity.
Open Finger Fracture
This young man sustained a open fracture of the finger. There was a large wound in the front of the finger.
We converted contaminated wound into a clean wound. Primary fixation of the fracture was done with fixation device. Our fixation method allows early finger movements with immediate wound closure, the gentleman made a full recovery.

Case Study



